All About Serious Infections
-
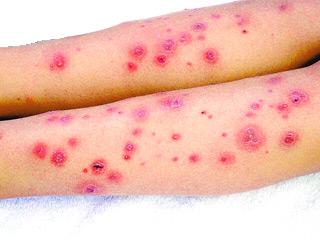 The picture at right is of serious bacterial infection from skin sores...
The picture at right is of serious bacterial infection from skin sores...
Did you know that your skin is the largest organ of your body? It is the largest in terms of weight between; 6 and 9 pounds, and 2 sq yards surface area. Your skin separates the inside of your body from the outside world.
- Skin protects you from bacteria and viruses which may cause infection
- Helps you sense the outside world, such as whether it is hot or cold, wet or dry
- Regulates your internal body temperature
- Click-here for Prevention of Serious Infections
Conditions that irritate, clog or inflame your skin can cause symptoms such as redness, swelling, burning and itching. Allergies, irritants, your genetic makeup and certain diseases and immune system problems can cause dermatitis, hives and other skin conditions. Many skin problems, such as acne, also affect your appearance.
Your skin helps protect you from germs, but sometimes it can get infected by them. Some common types of skin infections are
- Bacterial: Cellulitis and impetigo. Staphylococcal infections can also affect the skin.
- Viral: Shingles, warts, and herpes simplex
- Fungal: Athlete's foot and yeast infections
Your skin can also get parasites and other infections, such as head lice and human scabies.
Causes of Skin Infections
Staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria are the most common causes of cellulitis.
The skin normally has many types of bacteria living on it.
 When there is a break in the skin, however, bacteria can enter the body and cause infection and inflammation. The skin tissues in the infected area become red, hot, irritated, and painful.
When there is a break in the skin, however, bacteria can enter the body and cause infection and inflammation. The skin tissues in the infected area become red, hot, irritated, and painful.
Risk factors for cellulitis include:
- Cracks or peeling skin between the toes
- History of peripheral vascular disease
- Injury or trauma with a break in the skin (skin wounds)
- Insect bites and stings, animal bites, or human bites
- Ulcers from diabetes or a blockage in the blood supply (ischemia)
- Use of corticosteroid medications or medications that suppress the immune system
- Wound from a recent surgery
Symptoms of Infections
- Fever
- Signs of infection:
- Chills, shaking
- Fatigue
- General ill feeling (malaise)
- Muscle aches, pains (myalgias)
- Warm skin, sweating
- Pain or tenderness in the area with the rash or sore
- Skin redness or inflammation that increases in size as the infection spreads
- Skin sore or rash (macule):
- Comes on suddenly
- Grows quickly in the first 24 hours
- Usually has sharp borders
- Tight, glossy, "stretched" appearance of the skin
- Warmth over the area of redness
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease:
- Hair loss at the site of infection
- Joint stiffness caused by swelling of the tissue over the joint
- Nausea and vomiting
Exams and Tests for Skin Infections
During a physical examination, the doctor may find:
- Redness, warmth, and swelling of the skin
- Swelling and drainage if the infection is around a skin wound
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes) near the cellulitis
Your health care provider may mark the edges of the redness with a pen, to see if the redness goes past the marked border over the next several days.
Tests that may be used:
- Blood culture
- Complete blood count (CBC)
Treatment of Serious Skin Infection
Treatment for serious Cellulitis skin infection may require a hospital stay if:
- You are real sick (very high temperature, blood pressure problems, nausea and vomiting that does not go away)
- You have been on antibiotics and the infection is getting worse
- Your immune system is not working well (due to cancer, HIV)
- You have an infection near your eyes
Most of the time, treatment with oral antibiotics and close follow-up is enough. Treatment is focused on controlling the infection and preventing complications.
You may receive antibiotics to control the infection, and analgesics to control pain.
Raise the infected area higher than your heart to reduce swelling. Rest until your symptoms improve.
Outlook / Prognosis for Serious Infections
It is possible to be cured with 7 - 10 days of treatment. Cellulitis may be more severe in people with chronic diseases and those who are more prone to infection because their immune system is not working properly (immunosuppressed).
People with fungal infections of the feet may have cellulitis that keeps coming back. The cracks in the skin offer an opening for bacteria to get inside. Click-here for Health Tip-of-the-Day.
Possible Complications of Skin Infections
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Inflammation of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis)
- Meningitis (if cellulitis is on the face)
- Sepsis amd Shock
- Tissue death (gangrene)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if:
- You have symptoms of cellulitis
- You are being treated for cellulitis and you develop new symptoms, such as persistent fever, drowsiness, lethargy, blistering over the cellulitis, or red streaks that spread
Seek medical attention immediately if the cellulitis is on your face.




