All About Arthroscopic Surgery
 Knee arthroscopy is surgical procedure in which a small camera
is used to examine tissues inside the knee joint.
Knee arthroscopy is surgical procedure in which a small camera
is used to examine tissues inside the knee joint.
Arthroscopy surgery is often needed for both shoulder injury and knee injuries, frequently attributable to knee injury problems caused by sports, including running knee injuries.
Arthroscopy allows for the visualization of the interior of a joint through the use of optic instruments. Surgery can now be performed on larger joints using direct visualization and miniaturized techniques. After this procedure, the person can often go home the same day.
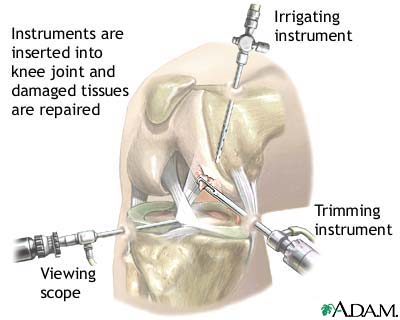
Arthroscopic surgery on the knee involves inserting a small camera, less than 1/4 inch in diameter, into the knee joint through a small incision. The camera is attached to a video monitor which the surgeon uses to see inside the knee, known as scoping.
In some medical facilities, the patient can even choose to watch the arthroscopic surgery on the monitor as well. Arthroscopic surgery can be seen in the operating room live and on medical television shows.
Make sure you bring your health insurance card with you so the doctor can determine if your health insurance fully covers arthroscopic surgery, which surgical and medical costs can be quite substantial.
For a simple surgical procedure, a local or regional anesthetic is administered, which numbs the affected area. The surgical patient remains awake and able to respond. For more extensive surgery, general anesthesia may be used. In this case the patient is unconscious and pain-free.
After the tiny arthroscopy camera is inserted, saline is pumped in under pressure to expand the knee joint and to help control bleeding. Some surgeons may also use a tourniquet to prevent bleeding.
After looking around (scoping) the entire knee for problem areas, the surgeon will usually make 1-4 additional small incisions to insert other instruments. Commonly used instruments include a blunt hook to pull on various tissues, a shaver to remove damaged or unwanted soft tissues, and a burr to remove bone. A heat probe may also be used to remove inflammation (synovitis) in the joint.
Additional instruments may be inserted to repair the knee. At the completion of the arthroscopy surgery, the saline is drained from the knee, the incisions closed, and a dressing applied. Many surgeons take pictures of the procedure from the video monitor to allow the patient to see what was done. If you ever had a bad experience with an intern, an M.D., surgical operating room, a Nurse, or The ER, you may want to consider becoming a Snitch for everyone's knowledge and benefit.
Indications that surgery may be needed
Arthroscopy knee surgery may be recommended for knee injury pain, and knee pain problems, such as:
- Torn meniscus (either repair or remove)
- Mild arthritis
- Loose bodies (small pieces of broken cartilage) in the knee joint
- A torn or damaged anterior cruciate or posterior cruciate ligament
- Inflamed or damaged lining of the joint (synovium)
- Misalignment of the knee cap (patella)
Risks of Arthroscopy Surgery
The risks for any anesthesia are - Allergic reactions to medications and breathing problems
The risks for any surgery are - Bleeding and Infection
Additional surgery risks include:
- Bleeding into the joint (hemarthrosis)
- Damage to the cartilage, meniscus, or ligaments in the knee
- Failure of the surgery to relieve symptoms
- Knee stiffness
Doctor and patient expectations after surgery
Since arthroscopy surgery is minimally invasive, it has reduced the need for the arthroscopic surgeon to surgically open the knee joint. As a result, it's resulted in less knee pain and leg stiffness, fewer medical complications, decreased length (if any) of hospitalization, and faster recovery time. Of course, expectations vary widely with the arthroscopic surgery. Click-here for Health Tip-of-the-Day.
Surgery done for a miniscule tear or loose bodies when the patient has no other problems (like arthritis) is usually uncomplicated, and most patients can expect a full recovery. The presence and effects of arthritis dramatically reduces the effectiveness of arthroscopy and consequently as many as 50% of arthroscopic surgery recipients may not improve post-operatively.
Arthroscopic removal of the synovium (arthroscopic synovectomy) can be of great benefit to patients with rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis pain. Arthroscopic or arthroscopic assisted surgery done to repair the meniscus or reconstruct ligaments in the injured knee is much more complicated with prolonged surgery recovery and more variable end-results.
Convalescence
For a simple meniscal cleaning (debridement), patient recovery is typically rapid. However, the arthroscopy patient may need to use crutches for a while to reduce weight placed on the knee joint to control knee pain. Pain can be managed with medications, including generic prescription drugs.
For more complicated procedures where anything is fixed or reconstructed such as joint replacement, patients may not be able to walk on the knee for several weeks, and the overall surgical recovery time is typically from several months to as long as one-year.




