![]()
Arteries Organization Working on Providing Healthy Arteries and Veins Knowledge Since Year 2006
Work on keeping your cardiovascular system, heart, arteries and veins healthy and unblocked by heart attack causing fatty arteru deposits starting today . . . What to do to keep your arteries healthy and non-blocked? A good diet and regular exercise will help prevent clogged arteries.
Exactly what Causes Heart Attacks?
People are searching for these terms: arteries, arterial anatomy, arterial blood flow, arterial circulation, arterial system, peripheral arteries, coronary arteries, carotid arteries, aorta, arterial stenosis, arterial hypertension, arterial disease, arterial embolism, arterial thrombosis, arterial plaque, arterial occlusion, arterial repair, arterial bypass surgery, arterial revascularization, endovascular procedures for arterial disease, arterial blood pressure measurement
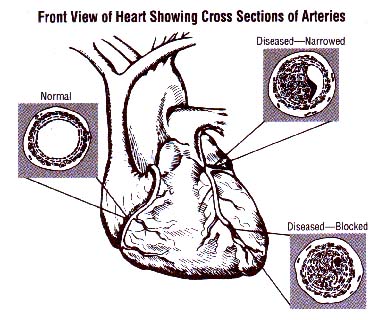
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot which ends-up blocking one of the coronary arteries (the blood vessels bring blood and oxygen to the heart muscle). When blood cannot reach part of your heart, the area starves for oxygen. If the blockage continues long enough, cells in the affected area die caused by arteriosclerosis.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the most common underlying cause of a heart attack. CAD is the hardening and narrowing of the coronary arteries by the buildup of plaque in the inside walls, which is known as arteriosclerosis (also known as atherosclerosis). Over an extended time, ongoing plaque buildup in the coronary arteries can:
- Narrow the arteries so that less blood flows to the heart muscle
- Completely block the arteries and the flow of blood
- Cause blood clots to form and block the arteries
A less common cause of heart attacks is a severe spasm (tightening) of the coronary artery that cuts off blood flow to the heart. These spasms can occur in persons with or without artery disease. Artery spasm can sometimes be caused by:
- Taking certain drugs, such as cocaine
- Emotional stress
- Exposure to cold
- Cigarette smoking
What Makes a Heart Attack More Likely?
Certain factors make it more likely that you will develop arteriosclerotic heart disease and get a heart attack. These are called risk factors.
The Heart and Arteries Health Risk Factors you are not able to change include:
- Your age (of course)
- Men: over age 45
- Women: over age 55
- Having a family history of early heart disease
- Heart disease diagnosed in father or brother before age 55
- Heart disease diagnosed in mother or sister before age 65
- Having a personal history of CAD
- Angina
- A previous heart attack
A surgical procedure (angioplasty, heart bypass) to
increase blood flow to your heart.
Risk factors that you can change include:
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Obesity
- Being physically inactive
- Diabetes (high blood sugar)
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
The warning signs and symptoms of a heart attack can include:
Chest discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes, or goes away and comes back. The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain. Heart attack pain can sometimes feel like indigestion or heartburn.
Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. Can include pain, discomfort, or numbness in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Shortness of breath. Often comes along with chest discomfort. But it also can occur before chest discomfort.
Other symptoms. May include breaking out in a cold sweat, having nausea and vomiting, or feeling light-headed or dizzy.
Signs and symptoms vary from person to person. In fact, if you have a second heart attack, your symptoms may not be the same as for the first heart attack. Some people have no symptoms. This is called a "silent" heart attack.
The symptoms of angina can be similar to those of a heart attack. If you have angina and notice a change or a worsening of symptoms, see your doctor fast.
Know the warning signs of a heart attack so you can act fast to get treatment. Many heart attack victims wait 2 hours or more after their symptoms begin before they seek medical help. This delay can result in death or long-lasting heart damage.
If you think you may be having a heart attack, or if your angina pain does not go away as usual when you take your angina medicine as directed, call 9-1-1 for help. You can begin to receive life-saving treatment in the ambulance on the way to the ER.
How is a Heart Attack Correctly Diagnosed?
The Right Diagnosis and treatment of a heart attack begins when the First Responders arrive after you call 9-1-1 so please don't delay calling 911 because you are not positive you are having a heart-attack.
 At the hospital emergency room, doctors will work fast
to find out if you are having or have had a heart attack.
They will consider your symptoms, medical and family
history and medical test results. Initial tests will be quickly
followed by treatment if you are having a heart attack.
At the hospital emergency room, doctors will work fast
to find out if you are having or have had a heart attack.
They will consider your symptoms, medical and family
history and medical test results. Initial tests will be quickly
followed by treatment if you are having a heart attack.
Tests used include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This test is used to measure the rate and regularity of your heartbeat. A 12-lead EKG is used in diagnosing a heart attack.
Blood tests. When cells in the heart die, they release enzymes into the blood. They are called markers or biomarkers. Measuring the amount of these markers in the blood can show how much damage was done to your heart. These tests are often repeated at intervals to check for changes. The specific blood tests are:
Troponin test. This test checks the troponin levels in the blood. It is considered the most accurate blood test to see if a heart attack has occurred and how much damage was done to the heart.
CK or CK-MB test. These tests check for the amount of the different forms of creatine kinase in the blood.
Myoglobin test. This test checks for the presence of myoglobin in the blood. Myoglobin is released when the heart or other muscle is injured.
Nuclear heart scan. This test uses radioactive tracers (technetium or thallium) to outline heart chambers and major blood vessels leading to and from the heart. A nuclear heart scan shows any damage to your heart muscle.
Cardiac catheterization. A thin flexible tube a.k.a. catheter, is passed through an artery in the groin or arm to reach the coronary arteries. Your doctor can determine pressure and blood flow in the heart's chambers, collect blood samples from the heart, and examine the arteries of the heart by x-ray.
Coronary angiography. This test is usually performed along with cardiac catheterization. A dye that can be seen using x-ray is injected through the catheter into the coronary arteries. Your doctor can see the flow of blood thru the heart and see where there are likely blockages.