Juvenile Diabetes
When Your Child Is Diagnosed with JUVENILE DIABETES
Today is which is a good date to start working on successful treatment of juvenile diabetes as medical research slowly works on a potential cure... Parents of children with juvenile diabetes naturally have serious concerns about the disease, its impact on their family, and how to keep their children safe and healthy. Use these questions to talk with your child's health care team and learn about your child's diabetes care needs at diagnosis and later on as well.
What are the different types of juvenile diabetes?
Which type of juvenile diabetes does our child have?
Will juvenile diabetes ever fade away?
Will my juvenile with type-1 diabetes always have to take insulin?
What are my child's treatment options and goals?
How can we help our child meet these goals?
How often will our child need to visit the doctor or specialist each year?
Who should be part of my child's health-care team and what role does each play in my kids care?
How can we work together as a family to help our child?
How can we help our child check glucose, take insulin, eat healthy foods and be more active?
Who can help us work together as a family unit?
What emotional issues might our child and family face?
Can juv diabetes affect our child's behavior and if so, how?
When do we start letting our child manage his/her own diabetes care?
Should we tell friends and family about our child's diabetes?
Who can help us if we don't have medical insurance?
What resources are there to help our child in school?
What does juv mean for other members of our family?
Does it mean our other children will get diabetes too?
What about other family members?
Who can help us cope with these issues?
For the ANSWERS to these questions, and more information visit https://ndep.nih.gov//teens/ParentsQuestions.aspx National Diabetes Education Program - YourDiabetesInfo.org - 1-888-693- 6337
Diabetes and Juvenile Diabetes
Juvenile diabetes is a complex disease with various causes. People with diabetes have high blood glucose levels, also called high blood sugar or hyperglycemia.
Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism which is the way the body uses digested food for energy. The digestive tract breaks down carbohydrates, sugars and starches found in many foods into glucose, a form of sugar that enters the bloodstream. With the help of the hormone insulin, cells throughout the body absorb glucose and use it for energy. Diabetes develops when the body doesn't make enough insulin or is not able to use insulin effectively, or both.
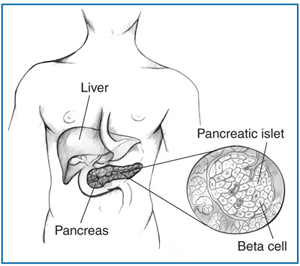 Insulin is made in the pancreas, which is an organ located behind the stomach. The pancreas contains clusters of cells called islets. Beta cells within the islets make insulin and release it into the blood. Islets within the pancreas contain beta cells, which make insulin and release it into the blood.
Insulin is made in the pancreas, which is an organ located behind the stomach. The pancreas contains clusters of cells called islets. Beta cells within the islets make insulin and release it into the blood. Islets within the pancreas contain beta cells, which make insulin and release it into the blood.
If beta cells don't produce enough insulin, or the body doesn't respond to the insulin that's there, glucose builds up in the blood instead of being absorbed by cells in the body, leading to prediabetes or diabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which blood glucose levels or A1C levels - which reflect average blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. In diabetes, the body's cells are starved of energy despite high blood glucose levels.
Over time, high blood glucose damages nerves and blood vessels, leading to complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, dental disease, even amputation. Other complications of diabetes may include increased susceptibility to other diseases, loss of mobility with aging, depression, and pregnancy problems. No one is certain what starts the processes that cause diabetes, but scientists believe genes and environmental factors interact to cause diabetes in most cases.
The two main types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. A third type, gestational diabetes, develops only during pregnancy. Other types of diabetes are caused by defects in specific genes, diseases of the pancreas, certain drugs or chemicals, infections, and other conditions. Some people show signs of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.

