![]()
Chronic, Severe or Serious Allergic Reaction and
Symptoms of Allergic Reaction Resource Center...
Serious, chronic or severe allergic reactions from things such as insect stings & bites, animal dander, certain foods, fish, drugs and medications, plants and pollens can be avoided today if you know what causes allergic reaction, so be informed about allergic reactions... Welcome to "Serious Allergic Reaction" your online health source for information about Serious Allergic Reaction ... We are on a mission of giving Serious Allergic Reaction relief to people who suffer from allergic reaction medical condition caused by allergies...
Allergic reactions are sensitivities to substances, called allergens, that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. They can be inhaled into the lungs, swallowed, or injected.
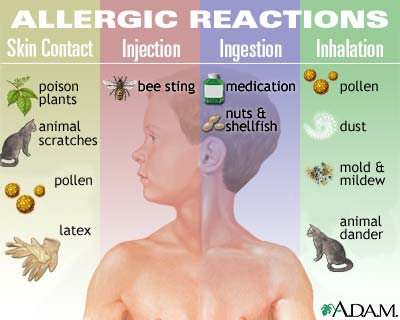
Allergic reaction can be provoked by skin contact with poison plants, chemicals and animal scratches, as well as by insect stings. Ingesting or inhaling substances like pollen, animal dander, molds and mildew, dust, nuts and shellfish, may also cause allergic reaction. Medications such as penicillin and other antibiotics are also to be taken with care, to assure an allergic reflex is not triggered.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions are more common than you would suspect. The human body's immune response causing a severe or serious allergic reaction is similar to the response that causes hay fever. Most reactions happen soon after contact with an allergen.
Many allergic reactions are mild, while others can be severe and life-threatening. They can be confined to a small area of the
 body, or they may affect the entire body. The most severe form is called anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock. Allergic reactions occur more often in people who have a family history of allergies.
body, or they may affect the entire body. The most severe form is called anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock. Allergic reactions occur more often in people who have a family history of allergies.
Substances that don't bother most people (such as venom from bee stings and certain foods, medications, and pollens) can trigger allergic reactions in some people.
Although first-time exposure may only produce a mild reaction, repeated exposures may lead to more serious reactions. Once a person has had an exposure or an allergic reaction (is sensitized), even a very limited exposure to a very small amount of allergen can trigger a severe reaction.
Most severe allergic reactions occur within seconds or minutes after exposure to the allergen. However, some reactions can occur after several hours, particularly if the allergen causes a reaction after it has been eaten. In very rare cases, reactions develop after 24 hours.
Anaphylaxis is a sudden and severe allergic reaction that occurs within minutes of exposure. Immediate medical attention is needed for this condition. Without treatment, anaphylaxis can get worse very quickly and lead to death within 15-minutes.
Causes for Allergic Reactions
Common allergens include:
- Animal dander
- Bee stings or stings from other insects
- Foods, especially nuts, fish, and shellfish
- Insect bites
- Medications
- Plants
- Pollens
Symptoms of Allergic Reactions
Common symptoms of a mild allergic reaction include:
- Hives (especially over the neck and face)
- Itching
- Nasal congestion
- Rashes
- Watery, red eyes
Symptoms of a moderate or severe reaction include:
- Cramps or pain in the abdomen
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Fear or feeling of apprehension or anxiety
- Flushing or redness of the face
- Nausea and vomiting
- Palpitations
- Swelling of the face, eyes, or tongue
- Weakness
- Wheezing
- Unconsciousness
First Aid for Allergic Reactions
For a mild to moderate reaction:
Calm and reassure the person having the reaction, as anxiety can worsen symptoms.
- Try to identify the allergen and have the person avoid further contact with it. If the allergic reaction is from a bee sting, scrape the stinger off the skin with something firm (such as a fingernail or plastic credit card). Do not use tweezers; squeezing the stinger will release more venom.
- If the person develops an itchy rash, apply cool compresses and over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream.
- Watch the person for signs of increasing distress.
- Get medical help. For a mild reaction, a physician may recommend over-the-counter medications (such as antihistamines).
For a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis):
- Check the person's airway, breathing, and circulation (the ABC's of Basic Life Support). A warning sign of dangerous throat swelling is a very hoarse or whispered voice, or coarse sounds when the person is breathing in air. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
- Call 911.
- Calm and reassure the person.
- If the allergic reaction is from a bee sting, scrape the stinger off the skin with something firm (such as a fingernail or plastic credit card). Do not use tweezers -- squeezing the stinger will release more venom.
- If the person has emergency allergy medication on hand, help the person take or inject the medication. Avoid oral medication if the person is having difficulty breathing.
- Take steps to prevent shock. Have the person lie flat, raise the person's feet about 12 inches, and cover him or her with a coat or blanket. Do NOT place the person in this position if a head, neck, back, or leg injury is suspected or if it causes discomfort.
DO NOT
- Do NOT assume that any allergy shots the person has already received will provide complete protection.
- Do NOT place a pillow under the person's head if he or she is having trouble breathing. This can block the airways.
- Do NOT give the person anything by mouth if the person is having trouble breathing.
When to Contact a Medical Professional for Allergic Reactions
Call for immediate medical emergency assistance if:
- The person is having a severe allergic reaction -- always call 911. Do not wait to see if the reaction is getting worse.
- The person has a history of severe allergic reactions (check for a medical ID tag).
Prevention of Allergic Reactions
- Avoid triggers such as foods and medications that have caused an allergic reaction (even a mild one) in the past. Ask detailed questions about ingredients when you are eating away from home. Carefully examine ingredient labels.
- If you have a child who is allergic to certain foods, introduce a new food, one at a time, in small amounts so you can recognize a chronic or serious allergic reaction.
- People who know that they have had serious allergic reaction should wear a medical ID tag.
- If you have a history of serious allergic reactions, carry emergency medications (such as a chewable form of diphenhydramine and injectable epinephrine or a bee sting kit) according to your health care provider's instructions.
- Do not use your injectable epinephrine on anyone else. They may have a condition (such as a heart problem) that could be negatively affected by this drug.
Recommended Health Resources
![]() Click-here for Health Tip-of-the-Day
Click-here for Health Tip-of-the-Day