Types of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs if an artery that supplies oxygen-rich blood to the brain becomes blocked. Blood clots often cause the blockages that lead to ischemic strokes.
The two types of ischemic stroke are thrombotic and embolic. In a thrombotic stroke, a blood clot (thrombus) forms in an artery that supplies blood to the brain.
In an embolic stroke, a blood clot or other substance, such as plaque, a fatty material travels through the bloodstream to an artery in the brain. A blood clot or piece of plaque that travels through the bloodstream is called an embolus.
With both types of ischemic stroke, the blood clot or plaque blocks the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the brain.
Ischemic Stroke
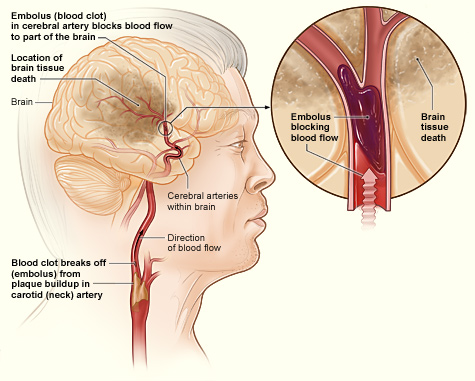
The illustration shows how an ischemic stroke can occur in the brain. If a blood clot breaks away from plaque buildup in a carotid (neck) artery, it can travel to and lodge in an artery in the brain. The clot can block blood flow to part of the brain, causing brain tissue death.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs if an artery in the brain leaks blood or ruptures (breaks open). The pressure from the leaked blood damages brain cells.
The two types of hemorrhagic stroke are intracerebral and subarachnoid. In an intracerebral hemorrhage, a blood vessel inside the brain leaks blood or ruptures.
In a subarachnoid hemorrhage, a blood vessel on the surface of the brain leaks blood or ruptures. When this happens, bleeding occurs between the inner and middle layers of the membranes that cover the brain.
In both types of hemorrhagic stroke, the leaked blood causes swelling of the brain and increased pressure in the skull. The swelling and pressure damage cells and tissues in the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
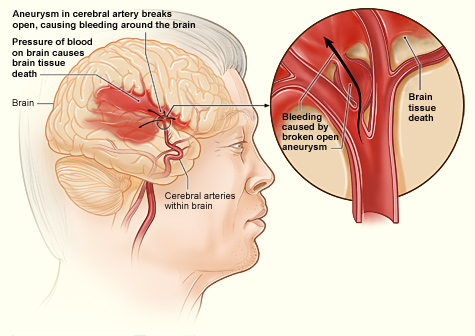
The illustration shows how a hemorrhagic stroke can occur in the brain. An aneurysm in a cerebral artery breaks open, which causes bleeding in the brain. The pressure of the blood causes brain tissue death.
The time it takes to recover from a stroke varies — it can take weeks, months, or even years. Some people recover fully, while others have long-term or lifelong disabilities.
Ongoing care, rehabilitation, and emotional support can help you recover and may even help prevent another stroke.
If you’ve had a stroke, you’re at risk of having another one. Know the warning signs of a stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) and what to do if they occur. Call 9–1–1 as soon as symptoms start.
Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. Call an ambulance so that medical personnel can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the emergency room. During a stroke, every minute counts.
